Llama 3.2: Simplificando a Aplicação de IA no Mundo Real

Recentemente, a XXAI atualizou sua plataforma integrando modelos avançados de IA, como o Llama 3.2. Muitas pessoas podem se perguntar como utilizar efetivamente esses poderosos modelos de IA em aplicações práticas e quais são as vantagens específicas de cada um. Para responder a essas perguntas, pesquisei e avaliei as informações mais recentes sobre esses modelos de IA. Neste artigo, fornecerei uma introdução detalhada ao Llama 3.2 e compartilharei algumas impressões baseadas na minha experiência.
O mais recente lançamento da Meta, Llama 3.2, não é apenas uma atualização de um modelo de linguagem; é um passo significativo em direção aos sistemas de IA multimodais. Llama 3.2 combina capacidades textuais e visuais, introduzindo quatro novos modelos: dois modelos de texto leves (1B e 3B) e dois modelos visuais (11B e 90B). Esses modelos marcam a ampla adaptabilidade do Llama 3.2 em aplicações de IA, oferecendo soluções para tarefas que vão desde a síntese de documentos extensos até a compreensão complexa de imagens.
Transição para um Sistema Multimodal
Com o rápido desenvolvimento da tecnologia de IA, os sistemas multimodais estão se tornando cada vez mais comuns. Llama 3.2 é capaz de processar tanto texto quanto imagens, realizando verdadeiramente as capacidades interdisciplinares da IA. Anteriormente, os modelos de IA só podiam lidar com texto ou imagens separadamente. No entanto, Llama 3.2 reforça as habilidades multitarefa da IA ao integrar o processamento de linguagem e imagens. Por exemplo, Llama 3.2 pode ler artigos extensos enquanto analisa o conteúdo das imagens, agindo como um assistente que pode compreender mapas e conversar com você.
Modelos de Texto Leves do Llama 3.2
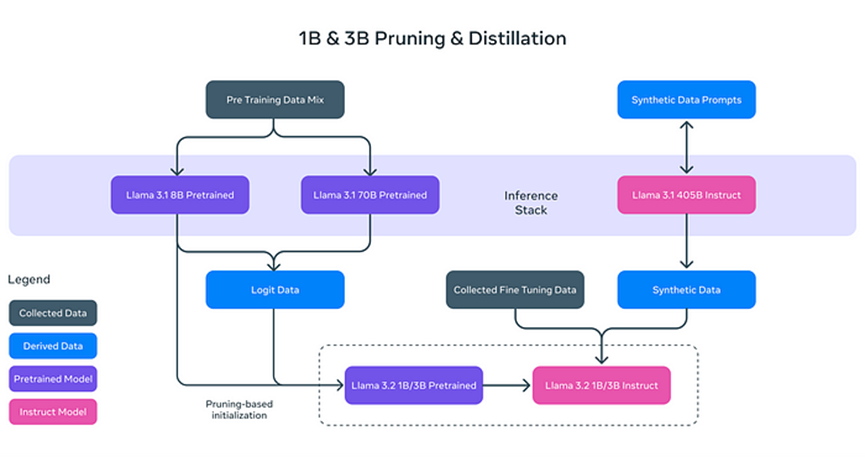
Os dois modelos de texto leves do Llama 3.2 (1B e 3B) são projetados para serem eficientes e podem manipular uma grande quantidade de informações contextuais em dispositivos locais. Por exemplo, o modelo 3B pode processar até 128.000 tokens de dados simultaneamente. Isso significa que os modelos leves podem executar tarefas como a síntese de documentos e reescrever conteúdos sem depender excessivamente de recursos computacionais poderosos.
Por que os modelos de texto do Llama 3.2 são "leves"? Não se trata simplesmente de reduzir o tamanho do modelo, mas de aumentar sua eficiência por meio de técnicas inovadoras:
- **Pruning (Poda):** Remove as partes não essenciais do modelo enquanto mantém seu desempenho e eficiência, similar a podar os galhos de uma árvore para um crescimento mais saudável e eficiente.
- **Distillation (Destilação):** Extrai e comprime o conhecimento de modelos grandes (como o 8B do Llama 3.1) em modelos menores, garantindo que as informações essenciais sejam mantidas.
Esses modelos leves não apenas melhoram a velocidade de processamento, mas também permitem que o Llama 3.2 funcione em dispositivos como smartphones e computadores pessoais, reduzindo significativamente as exigências de hardware para as aplicações de IA.
Pós-Treinamento: Ajuste Fino e Alinhamento
Após a poda e destilação, os modelos de texto do Llama 3.2 passam por uma otimização pós-treinamento para melhorar seu desempenho em tarefas reais. Isso inclui:
- **Fine Tuning Supervisionado (SFT):** O modelo aprende de forma minuciosa a se desempenhar com maior precisão em diversas tarefas, como síntese de documentos e tradução de textos.
- **Rejection Sampling (RS):** Gera múltiplas respostas possíveis e seleciona a de melhor qualidade.
- **Direct Preference Optimization (DPO):** Classifica as respostas geradas de acordo com as preferências do usuário, oferecendo respostas mais alinhadas às suas necessidades.
Esses passos de pós-treinamento permitem que o Llama 3.2 lide com tarefas textuais complexas e forneça as respostas mais adequadas para diferentes problemas.
Capacidades Visuais do Llama 3.2
Outro ponto de destaque do Llama 3.2 são seus poderosos modelos visuais. Com a introdução dos modelos 11B e 90B, o Llama 3.2 pode analisar e interpretar conteúdo de imagens, além de compreender texto. Por exemplo, Llama 3.2 pode reconhecer informações visuais complexas em imagens e realizar "localização visual" com base em descrições. Essa capacidade é especialmente útil em campos como medicina e educação.
O modelo visual do Llama 3.2 utiliza a tecnologia de **Pesos de Adaptadores (Adapter Weights)**, permitindo uma integração fluida entre os codificadores de imagens e os modelos de linguagem. Isso permite que Llama 3.2 compreenda simultaneamente texto e imagens, e utilize ambas as fontes para realizar inferências. Por exemplo, um usuário pode carregar uma foto de um menu de restaurante e o Llama 3.2 pode destacar os pratos relevantes de acordo com as preferências do usuário (como "vegetariano").
Comparação com Outros Modelos Multimodais
O código aberto e a capacidade de personalização do Llama 3.2 lhe conferem uma posição única no mercado. Em comparação com o GPT da OpenAI, que também suporta o processamento de texto e imagens, o Llama 3.2 oferece maior flexibilidade, pois as versões multimodais do GPT geralmente são de código fechado e não são facilmente personalizáveis. Enquanto o PixTral da Mistral é relativamente leve, o Llama 3.2 ainda se destaca em termos de flexibilidade e capacidade de personalização.
Llama 3.2 não só gerencia tarefas de texto e imagem, mas também pode ser ajustado de forma precisa de acordo com as necessidades do usuário, atendendo às demandas de aplicações personalizadas.
Cenários de Aplicação Real
A capacidade multimodal do Llama 3.2 demonstra um potencial significativo em diversos campos:
- **Síntese de Documentos:** Graças aos seus modelos de texto leves, Llama 3.2 pode resumir rapidamente grandes quantidades de documentos ou arquivos PDF, extraindo informações chave.
- **Descrição de Imagens:** Llama 3.2 pode gerar automaticamente legendas de imagens precisas, ajudando os usuários a entender melhor o conteúdo visual.
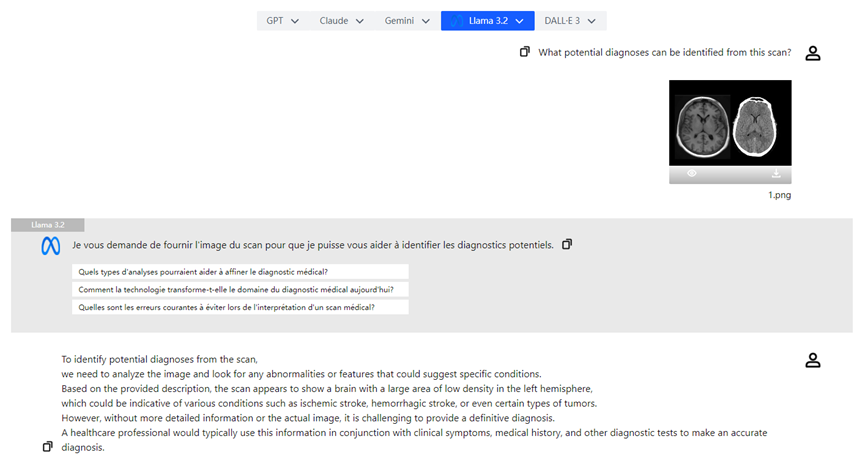
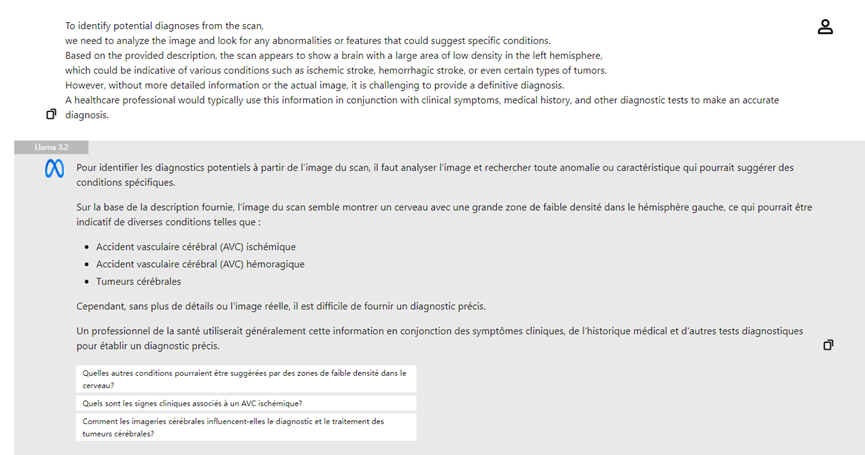
- **Análise de Imagens Médicas:** Médicos podem carregar radiografias e o modelo visual do Llama 3.2 pode ajudar na análise, destacando áreas de possível preocupação e melhorando a eficiência do diagnóstico.
Conclusão
Llama 3.2 representa um grande avanço na tecnologia de inteligência artificial. Ao melhorar a velocidade e eficiência de processamento com modelos de texto leves e realizar inferências multimodais com modelos visuais, essas inovações simplificam ainda mais as tarefas diárias e desbloqueiam o vasto potencial da IA em várias indústrias. A implementação do Llama 3.2 torna a tecnologia de IA mais acessível, oferecendo uma ampla gama de cenários de aplicação, desde a síntese de documentos até a compreensão de imagens. Com o contínuo desenvolvimento da tecnologia de IA, não há dúvida de que o Llama 3.2 desempenhará um papel cada vez mais importante em diversos setores.