Differences Between Artificial Intelligence and Generative Artificial Intelligence

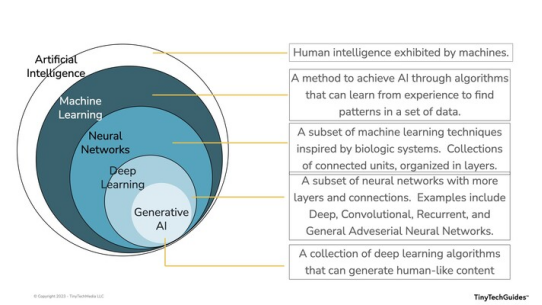
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI) are two powerful branches of computer science that have become integral parts of our daily lives. While both AI and Generative AI are transforming a wide range of industries, their functionalities differ significantly. Understanding these differences is essential for fully leveraging their potential. In this article, you'll discover the distinctions between AI and Generative AI, as well as future advancements that could further drive the development of AI.

What is Traditional Artificial Intelligence?
Traditional Artificial Intelligence (also known as narrow or weak AI) focuses on performing predefined tasks using predetermined algorithms and rules. These systems are typically trained on large datasets and learn to identify patterns in the data, using these patterns to make predictions or generate outputs. The effectiveness of traditional AI depends on the data used to train the algorithms. Traditional AI is designed to excel at a single activity or a limited set of tasks. Popular examples of traditional AI include Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems and voice assistants like Siri or Alexa, recommendation engines on platforms such as Netflix or Amazon, and Google's search algorithms. All these systems are trained to follow specific rules to provide useful information but do not create anything new.
What is Generative Artificial Intelligence?
Generative AI can be considered the next generation of AI. It is a type of AI capable of creating new content. Generative AI is an AI that can produce outputs such as text, images, and other data. This type of AI works primarily by analyzing large amounts of existing data and generating new content based on these findings. This means Generative AI relies on machine learning to identify, predict, and create content based on the datasets it accesses.
For example, OpenAI's GPT-4 language model is a quintessential Generative AI model. It is trained on massive internet data and can produce human-like text that is nearly indistinguishable from human writing.
Characteristics of Traditional Artificial Intelligence
The primary characteristics of narrow AI include:
- Programmed Intelligence: Traditional AI uses pre-programmed algorithms and rules. The system operates within the boundaries of algorithms developed by programmers to complete tasks and provide solutions.
- Limited Applications: These AI models are designed for specific tasks, limiting their potential application scope.
- Data Analysis: Traditional AI focuses on analyzing datasets and making predictions based on the analysis. It is effective in tasks like pattern recognition, predictions, and data analytics.
- Limited Learning Capability: Traditional AI's learning capacity is limited and relies on datasets created by human developers.
Characteristics of Generative Artificial Intelligence
Some of the most important characteristics of Generative AI include:
- Neural Network Generators: Generative AI uses neural network architectures like GAN (Generative Adversarial Networks) and VAE (Variational Autoencoders) to generate relevant and original outputs.
- Versatile Applications: These AI models are versatile, capable of producing various types of content, and find applications across numerous industries.
- Prompt-Based Content Creation: Generative AI creates content based on data and user inputs (prompts), rather than merely analyzing existing data. Its outputs are unique and tailored to the suggestions or instructions given.
- Adaptability: Generative AI can analyze prompts and datasets to produce new and original information, offering a broader range of applications.
Key Differences Between Artificial Intelligence and Generative Artificial Intelligence
The primary differences between traditional AI and Generative AI lie in their outputs and applications. While traditional AI systems are mainly used for data analysis and prediction, Generative AI goes a step further by creating new data similar to its training data.
Major Differences
- Traditional AI: Operates within a limited scope and focuses on tasks like pattern recognition, prediction, and specific data-driven activities (e.g., numeric predictions).
- Generative AI: Creates original content (e.g., text, code, music, audio, video, data) based on human inputs and data analysis.
Applications
- Traditional AI: Commonly used for tasks like spam filtering, fraud detection, and recommendation systems.
- Generative AI: Suitable for various general-purpose use cases and applications, such as answering complex questions, creating original images, music generation, video production, and other forms of content creation.XXAI is an AI software supported by 13 popular models like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity, and DALLE-3. It enhances writing, communication, and productivity. No matter where you work, you can access features such as summarization, answers, article refinement, translation, drafts, and AI search. With seamless switching between 13 models for professional content, XXAI saves hours for you every day.

Transparency
- Traditional AI: Operates based on predefined rules, making its decision-making process more transparent and easier to explain.
- Generative AI: Due to the complexity of its learning algorithms, Generative AI is less transparent, making it difficult to understand how specific outputs are generated.
Overall, while traditional AI excels in analyzing and interpreting data, Generative AI can perform tasks that traditional AI cannot. Generative AI creates new media, offers a broader range of applications, and transforms various industries.
Advantages and Limitations of Traditional AI
Advantages
- Reliability: Traditional AI systems often produce consistent and predictable results with the same input data, as they rely on predefined rules.
- Scalability: These systems can handle larger datasets or more complex decision-making processes without a proportional increase in costs or resources.
- Transparency: Rule-based AI systems are generally more transparent and explainable compared to Generative AI models.
- Specialization: Traditional AI performs well in fields where human experts can define precise decision-making rules and understanding.
Limitations
- Limited Flexibility: Traditional AI models struggle to adapt to new or unforeseen scenarios, which can make them less effective in dynamic environments.
- Lack of Creativity: Traditional AI is constrained by its pre-programmed rules, meaning it cannot generate new ideas, content, or solutions outside of its defined scope.
- Narrow Focus: These systems generally cannot generalize knowledge beyond the specific rules provided, making them less versatile.
- Transparency and Interpretability: Although transparent in some cases, certain traditional AI systems (especially deep learning models) can still lack clear interpretability.
Advantages and Limitations of Generative AI
Advantages
- Creativity: Generative AI can produce creative and innovative content by learning patterns from existing data.
- Adaptability: It can adapt to changing data and environments without the need for manual rule updates, continuing to improve its performance with more data.
- Data Augmentation: Generative AI can generate synthetic data to enhance existing datasets, which is particularly useful in data-scarce environments.
- Personalization: By generating tailored content, Generative AI provides a highly personalized experience for users.
Limitations
- Lack of Transparency: Opacity is a concern, as the internal workings of deep learning models are often difficult to explain, leading to challenges in understanding decision-making.
- Ethical Concerns: Generative AI can be misused to create deepfake content and other potentially harmful outputs, raising ethical challenges related to misinformation and abuse.
- Quality Control: Ensuring the quality of generated content can be challenging, particularly because Generative AI is notorious for producing false information.
- Bias: Generative AI models may unintentionally learn and propagate biases present in their training data, resulting in unfair outcomes.
Future of Traditional AI and Generative AI
Both traditional AI and Generative AI demonstrate significant potential for addressing complex, multifaceted real-world scenarios.
Future of Traditional AI
The future of traditional AI will focus on enhancing the adaptability of rule-based systems, making them more flexible to address unforeseen situations. Self-improving AI systems, achieved through reinforcement learning and dynamic analytics for self-optimization, will also play a key role in boosting adaptability and efficiency.
Future of Generative AI
At the same time, the future of Generative AI is bright, revolutionizing content creation and personalized customer communication by improving the quality and efficiency of generated outputs. The rise of multimodal AI models, which can understand and generate content in multiple forms of data, promises more immersive and natural experiences for users.
In Summary
Both Generative AI and traditional AI have unique advantages. While traditional AI focuses on analyzing and predicting specific tasks, it remains crucial. Generative AI finds widespread applications in areas like entertainment, e-commerce, and marketing. The two may complement each other in the future to solve complex problems. Artificial intelligence will continue to evolve in the future. If you're interested in Generative AI, XXAI can be your go-to platform.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Generative AI use deep learning?
Yes, Generative AI relies heavily on deep learning because it can create new and realistic content. In fact, specific deep learning architectures such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) and Variational Autoencoders (VAE) are specifically designed for generative tasks.
Can Generative AI make predictions?
Generative AI can be used for limited forms of prediction, but this is not its primary function, and it has more limitations compared to dedicated predictive AI models.
Conclusion
Generative AI and Traditional AI represent two distinct approaches to artificial intelligence, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Generative AI uses data-driven learning to provide creativity, adaptability, and potential for generalization. On the other hand, Traditional AI excels in domains with clear rules and specific expertise, offering transparency and reliability. As AI continues to evolve, these two paradigms may complement each other, driving innovation and progress in the field.