What is an AI Agent? | How Intelligent Assistants Are Changing Our Lives and Future

“Hey Siri, can you turn up the volume?” This simple voice command represents a turning point in the technology era. Starting from virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, our interaction with technology has been completely rewritten. The boundaries between humans and machines have become increasingly blurred.
Suddenly, we can not only chat with our friends and family but also converse with AI agents that understand us, respond quickly to our needs, and fulfill our requests. Today, AI agents are no longer fantasies from science fiction movies; they have become a norm in our daily lives. They reside in our phones, homes, cars, and even workplaces, quietly learning, adapting, and evolving to provide us with better services. So what exactly are these AI agents? How do they operate? In this article, we will delve into the world of AI agents, understand their capabilities, and explore their significant impact on our lives.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent, also known as an intelligent agent, is a software system that can operate autonomously, perceive its environment, and take actions to achieve specific goals. These agents leverage artificial intelligence technologies (such as machine learning, natural language processing, decision algorithms, etc.) to interact with the surrounding environment or users, interpret data, and make rational decisions.
Core Characteristics of AI Agents
- Autonomy: AI agents can operate independently and make decisions and execute tasks without human intervention.
- Perception Ability: They can sense and understand their environment through sensors, data inputs, or interactions with users.
- Decision-Making Ability: AI agents analyze data using advanced algorithms and AI technologies to select the optimal course of action to achieve their goals.
- Adaptability: AI agents can adjust based on changes in the environment or user needs, learning from experiences to continuously improve.
Examples of AI Agents
Chatbots
AI chatbots can interact with users, understand natural language, and provide relevant responses or execute tasks. For example, businesses use AI chatbots like XXAI to answer customer questions, provide product information, or help troubleshoot issues, greatly enhancing the customer service experience.
Self-Driving Cars
Self-driving cars developed by Tesla and Waymo rely on AI agents to perceive their environment, make driving decisions, and ensure vehicle safety. These vehicles utilize AI algorithms, sensors, and cameras to detect obstacles, recognize traffic signs, and adjust driving behavior.
Virtual Personal Assistants
Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are typical AI agents. They understand user commands and execute tasks, serving as our daily "helpers." Whether it's setting reminders, searching for information, or controlling smart homes, they make life easier and more convenient.
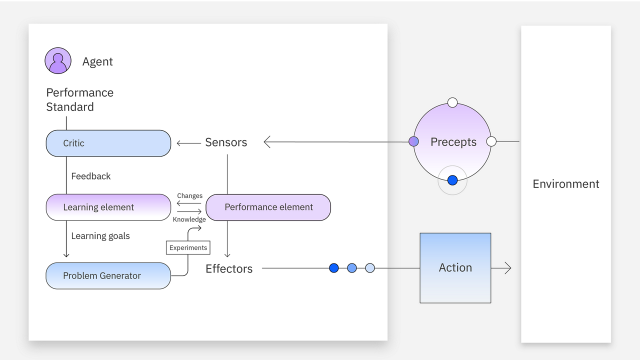
How Do AI Agents Work?
The core of AI agents is based on large language models (LLMs), and they are often referred to as LLM agents. Traditional LLMs (such as the IBM® Granite™ model) rely on training data for response generation, which has certain limitations in knowledge and reasoning capabilities. The uniqueness of agent technology lies in its ability to use backend tool calls to access the latest information, optimize workflows, and autonomously create subtasks to achieve complex objectives.
This automation capability allows AI agents to continuously learn about user needs over time, store past interaction data, and take more precise actions in the future, providing a more personalized experience. This makes them not just task completers, but guides for users to develop in more efficient and intelligent directions.
The work of AI agents can be divided into three main stages:
- Perception: AI agents perceive their surroundings through sensors or data inputs to gather information. This forms the basis for understanding dynamic conditions and adapting to change.
- Thinking and Decision-Making: After collecting data, AI agents use reasoning abilities to analyze situations, draw conclusions, and select the best course of action. This usually involves complex algorithmic computations and search analyses.
- Action: After thinking, AI agents take action. These actions may involve executing tasks, solving problems, or adapting to new challenges.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be divided into several different types, ranging from the simplest to the most complex:
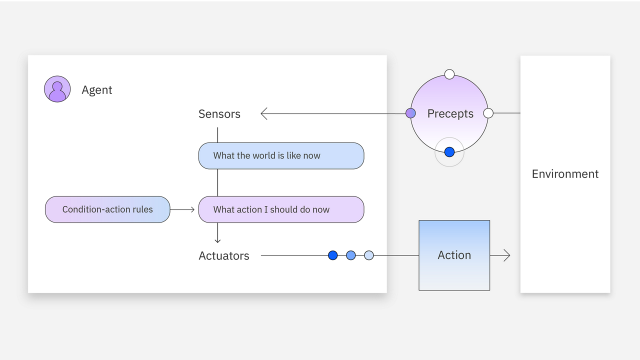
Simple Reflex Agents
The most basic type of agent that acts based on current perceptions. Such agents do not retain any memory and will not interact with other agents if information is lacking. If an agent encounters an unforeseen situation, it cannot respond appropriately. Agents only work in completely observable environments where access to all necessary information is allowed.
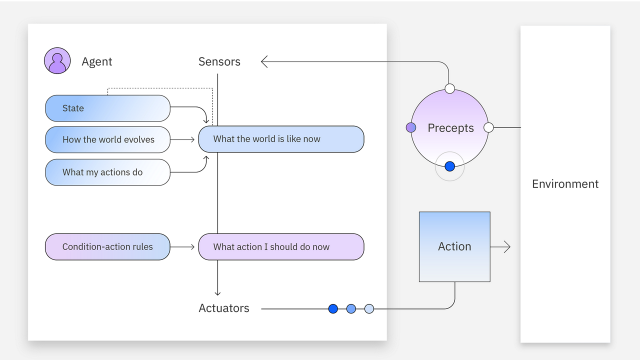
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Compared to simple agents, this type of agent can build internal models based on perceptions and memories, adapting to partially observable environments. However, they are still limited by a set of rules.
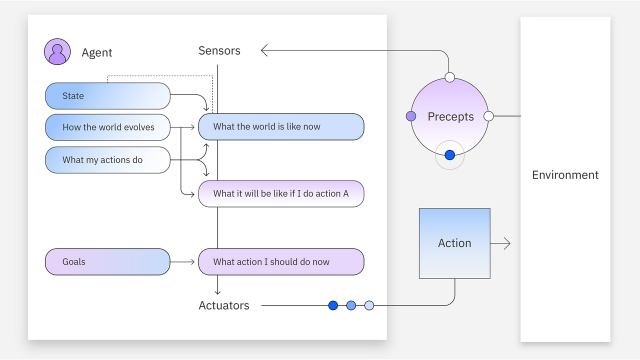
Goal-Based Agents
These agents have their own goals and will plan actions to achieve them, exhibiting greater flexibility. This search and planning enhance their efficiency compared to simple and model-based reflex agents.
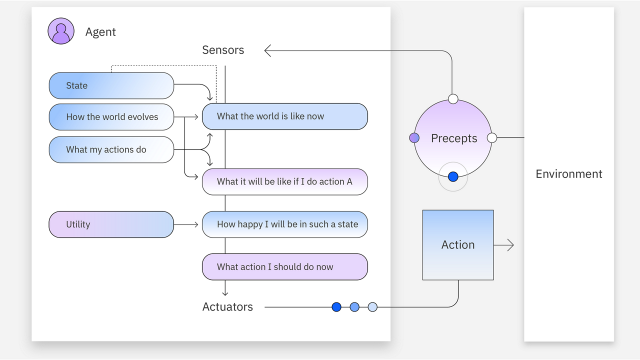
Utility-Based Agents
This type of agent not only has goals but also considers the utility of achieving those goals, choosing the most efficient path. Therefore, these agents are especially useful in scenarios where multiple scenes must meet desired goals and the best scenario must be chosen.
Learning Agents
The most complex type of agents, they not only adapt to the environment but continually optimize themselves through learning. New experiences are automatically added to their initial knowledge base, enhancing their ability to operate in unfamiliar environments.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence Agents
Artificial intelligence agents are showcasing their tremendous potential in various fields by improving work efficiency, enhancing decision-making capabilities, and improving customer experiences, fundamentally changing our lives. Let’s explore the significant advantages brought about by these AI agents in detail:
Improving Efficiency and Productivity
AI agents automate tedious and repetitive tasks, creating more time for human employees to focus on more complex and creative work. This approach not only optimizes workflows and reduces the frequency of human error but also greatly simplifies the processing of large amounts of data, improving communication quality and user satisfaction. More importantly, AI agents can operate continuously around the clock, ensuring availability at all times.
Optimizing Decision-Making and Reducing Operating Costs
With powerful data analysis capabilities, AI agents can identify potential patterns and trends, helping enterprises make better informed choices. Customized AI agents can also make real-time adjustments and provide recommendations for next steps, thereby optimizing business processes. The high productivity resulting from this automation directly leads to reduced operating costs for companies.
Enhancing Customer Experience
AI agents can provide highly personalized interaction experiences by analyzing customer preferences and behaviors. They are always on standby to assist customers, answer questions, and provide tailored recommendations, significantly boosting customer loyalty and satisfaction. Furthermore, the proactive problem-solving abilities of AI agents can anticipate issues before they occur and take preventive measures promptly.
Personalized Virtual Assistants
AI agents are always available, committed to providing comprehensive assistance to users. They can tailor interaction content based on user preferences and help arrange, remind, and organize daily tasks, significantly improving individual work efficiency.
Intelligent Health Companions
In the healthcare field, AI agents hold enormous potential. They can monitor patients’ health data and provide real-time updates to healthcare providers. These agents analyze personal health conditions, offer personalized health recommendations, and even assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing diseases.
Advanced Educational Tools
AI agents personalize educational content based on students’ learning styles and progress, thereby improving the overall learning experience. Through simulations, virtual reality, and adaptive learning platforms, AI agents offer interactive learning experiences while analyzing learning performance to provide insights and personalized suggestions to educators, helping them enhance teaching quality.
Home Management Systems
AI agents can autonomously perform various home management tasks, such as controlling smart devices, adjusting indoor temperatures, and managing energy consumption. They can integrate with home security systems, enhancing the sense of security at home. Additionally, AI agents simplify daily affairs, improve convenience, and significantly enhance the overall life experience at home.
Financial Investment Advisors
AI agents analyze financial data and provide personalized investment advice based on individual risk tolerance and financial goals. They can also monitor market trends and provide real-time insights to optimize investment strategies. Moreover, AI agents can assess and manage investment risks, providing users with informed decision-making support.
Autonomous Execution Agents
AI agents can independently complete complex tasks in various fields, thereby reducing the need for human intervention. Through data-driven decision-making support, not only can they improve efficiency, but they can also enhance work processes through continual learning and optimization.
Customized AI Agent for You - XXAI
XXAI is a multifunctional AI chatbot building tool that requires no programming skills. It utilizes powerful models like GPT-4 and Claude 3.5 to provide users with natural communication capabilities, emotional recognition, and adaptability, thereby enhancing productivity.

Key Features of XXAI:
- Innovative: Powered by dual AI models (GPT-4 and Claude 3.5), enhancing adaptability across various task scenarios.
- Comprehensive Toolset: Includes AI article writing tools, interpretation tools, text expanders, etc., to meet a wide range of content creation needs.
- Personalized Customization: Users can upload their own prompt libraries and adjust the generated content based on specific keywords and industry terminology, ensuring alignment with brand voice and style.
- Advanced Learning Capability: Continuously improves interactions with customers using artificial intelligence and machine learning, making the chatbot increasingly intelligent.
- User-Friendly: Compatible with both Windows and macOS, seamlessly integrating into applications or websites for various purposes, such as content generation and information summarization.
Diverse Applications of XXAI in Industries
- Customer Support: XXAI excels in providing around-the-clock assistance and resolving common issues, streamlining customer support processes.
- E-commerce: Offers personalized product recommendations, guiding users through purchasing processes and improving conversion rates.
- Code Assistance: Whether generating, optimizing, or debugging code, XXAI helps developers streamline software development processes and reduce error rates.
- Healthcare: It serves as a valuable resource by providing personalized and intelligent interactions in the healthcare sector.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations of Artificial Intelligence Agents
As AI agents are applied across various fields, despite bringing tremendous changes and advantages, they also face some complex challenges and significant ethical issues. These problems not only impact the development of AI technology but also relate to user trust, privacy, and safety, and thus require careful handling.
1. Security and Privacy Challenges
Unauthorized Autonomous Systems
AI agents operating without authorization can pose severe security risks. Imagine a self-operating system being maliciously manipulated or abused, which could not only impact personal privacy but also threaten the security of the entire system.
Data Privacy Risks
With the deepening applications of AI, data privacy issues have become particularly prominent. Generative artificial intelligence relies on vast amounts of data, and how to use personal information while ensuring data security is a critical challenge that must be addressed. Therefore, setting strict rules and protective measures is particularly important.
Transparency and Accountability
The popularity of AI agents requires their operational processes to be more transparent. Users and businesses need to understand how these systems make decisions and who should be responsible for their actions. Ensuring clear accountability is fundamental to ensuring that AI systems adhere to ethical standards.
2. Ethical Considerations in AI Integration
Building a Culture of Trust
The application of AI technology needs to find a balance between trust and responsibility. Businesses must ensure that the operation of AI agents aligns with users' values, building a culture based on transparency and trust to gain user confidence in the long run.
Protecting Human Rights
Human rights must always be at the core of the development and application of AI technology. To avoid potential social harms, businesses and policymakers need to establish specific guidelines to ensure that AI technology does not threaten basic human rights.
Shared Responsibility
The development and use of AI systems should not be solely the responsibility of designers and developers. All stakeholders, including users, businesses, and governments, need to work together to promote the ethical application of AI technology and continuously monitor its impact in the real world.
3. Eliminating Bias and Discrimination
Inclusivity and Fairness
The design of AI systems must take inclusivity and fairness into account to avoid bias against certain groups. A fair AI system serves all users better and helps avoid social issues caused by unfair decisions.
Reducing Algorithmic Bias
AI algorithms are not perfect. Continuous monitoring and auditing are necessary to avoid the emergence of biases during operation. By identifying and correcting biases, AI agents can ensure fair service for all users.
Formulating Ethical Guidelines for AI Use
To ensure the ethical use of AI systems, businesses and governments should work together to create comprehensive usage guidelines. These guidelines should include data transparency, public oversight, and strategies to address misinformation, ensuring the ethical application of AI technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does artificial intelligence (AI) fully realize its capabilities?
Artificial intelligence achieves its powerful capabilities by integrating large data sets with intelligent algorithms (essentially sets of instructions). This combination allows AI software to recognize patterns and features in data and to learn on its own, as noted by SAS in their introductory book on artificial intelligence.
What is the operating principle of AI agents?
The core purpose of AI agents is to perceive the surrounding environment and take corresponding actions to achieve predetermined goals. These agents efficiently operate using various artificial intelligence technologies, flexibly responding whether they are based on software or physical entities.
Do artificial intelligence agents represent the direction of future development?
Absolutely! As technology continues to advance, AI agents will assume increasingly important roles, subtly transforming industry landscapes and enhancing user experiences.
Summary
AI agents, with their unique charm, are changing our lives and integrating into various industries. From automating tasks to personalizing user experiences, AI agents bring us unprecedented convenience and efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, the role of AI agents will become increasingly important, reshaping societal landscapes and becoming a core force in the intelligent era.